Mesopotamia, an ancient Greek term meaning “the land between rivers,” or “the land between the two rivers” was the world’s first civilization, where the two rivers mentioned above are the Tigris and the Euphrates. With a very rich history, ancient Mesopotamia is the provenance of civilization or “cradle of civilization” as it was the place of origin for many things for instance agriculture, language, cities, religion and government.
Timeline of Mesopotamia begins with the earliest evidence of human culture around 5000 BC. During 4700 BC which is also known as the hassunah period was recognized for the earliest pottery making culture. Moving towards 4400 BC came the Halaf period where in addition to pottery making culture there was the add-on of the knowledge of metal in the process.
The Tigris River is one of the rivers along with the river Euphrates that defines Mesopotamia. The river Tigris is on the eastern side of Mesopotamia which is 1,150 miles long and at its widest point, the Tigris is 1,300 feet, the Sumerians knew the Tigris as the Idigna, which may be translated as “the swift river.”
In ancient Mesopotamia, there were a lot of crops to grow. But the floods in that region were very destructive, violent and unpredictable. The climate was also not suitable for farming throughout the year.
The climate of Mesopotamia was generally dry and there was very little rainfall so all these factors contributed to unsuccessful farming in this region. So to overcome this problem of farming Mesopotamians became depended on the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers.
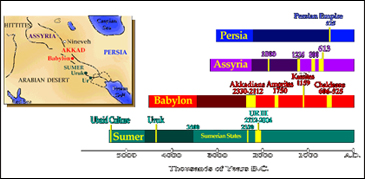
Two cultural groups form the principle elements in the population of Mesopotamia before the beginning of history and in the millennium thereafter (the 3rd millennium BC). These are the Sumerians and the Akkadians. They lived peacefully together. Mesopotamian sources in all periods seem to be free of strong racial ideologies or ethnic stereotypes.
It is interesting to study their technological innovations and scientific advances. The two rivers Tigris and Euphrates necessitated the invention of sail boats and canals. The people of Mesopotamia were discoverers of variety of things like the plough, cuneiform script, the algebra system, the calendar etc.
Symbols & Meanings
Mesopotamia Today
Images
Weapons Used
Writing System
Contributions / Achievements
Agriculture Methods
Popular Animals
Religious Beliefs
Buildings / Structures
Social Classes
Weather / Climate
Trade & Economy
Languages Invention
Leaders in Mesopotamia
Music & Instruments
Importance of Priests
Major Sculptures
Slaves & Slavery
Science & Technology
Temples Ziggurats
Tools used – Stone,Bone,Metal
Wars Fought
Role of Women
Architecture Mesopotamia Ancient
Blank Map Mesopotamia
Characteristics Of Mesopotamia
Cities In Mesopotamia
Compare and Contrast Mesopotamia and Egypt
Cultures Of Mesopotamia
Daily Life Of Mesopotamia
Define Mesopotamia Cradle Of Civilization
Education In Mesopotamia
Egypt And Mesopotamia Differences
Empires Of Mesopotamia
Kings Of Mesopotamia
Modern Mesopotamia
Rules Of Mesopotamia
Uruk Mesopotamia
Websites On Mesopotamia


